X-59 Unveiled at Lockheed Skunk Works: It Could Be a Game Changer
The future of supersonic commercial flight came into focus as aerospace giant Lockheed Martin rolled out the X-59, a unique experimental aircraft designed to quiet the sonic boom, at a ceremony in Palmdale, California.
The future of supersonic commercial flight came into focus on Friday, as aerospace giant Lockheed Martin rolled out the X-59, a unique experimental aircraft designed to quiet the sonic boom, at a ceremony in Palmdale, California. The ceremony, which was attended by Lockheed Martin, NASA and government leaders, marked a significant milestone in the company's and NASA's decades-long journey to solve one of the most persistent challenges of supersonic flight – the sonic boom.
This is not a render.
This is the X-59, a single-seat X-plane aiming to reduce the sound of the sonic boom to a mere thump. It opens the possibility for commercial supersonic flights over land, which has been prohibited since 1973. Be on the lookout for first flight! pic.twitter.com/7MZQZoyVjG
— Lockheed Martin (@LockheedMartin) January 12, 2024
"We're thrilled to take on this challenge alongside NASA, whose quiet supersonic technology mission will have lasting, transformational impacts for people around the world," said John Clark, vice president and general manager, Lockheed Martin Skunk Works. "This project is just one example of the broader ingenuity of our industry as we continually strive to push the envelope of what's possible."
Rollout ceremonies for high-profile aircraft have become a long-standing aviation tradition, and in the case of the X-59, it celebrated technical advancements, collaboration and innovation that stemmed from years of research, development and production of a one-of-a-kind technology demonstrator aircraft that will reduce the loudness of sonic booms to a gentle thump.
"The entire X-59 team leaned into the expertise of both legendary organizations, NASA and Lockheed Martin, to ensure success for this program. I am extremely proud of everyone who made this historic moment possible," said Greg Ulmer, executive vice president, Lockheed Martin Aeronautics.
Images of the X-59 were shared on X, the social media platform formerly known as Twitter, with @Lockheed Martin tweeting, "This is not a render. This is the X-59, a single-seat X-plane aiming to reduce the sound of the sonic boom to a mere thump. It opens the possibility for commercial supersonic flights over land, which has been prohibited since 1973. Be on the lookout for first flight!"
X-59: Revolutionizing Air Travel
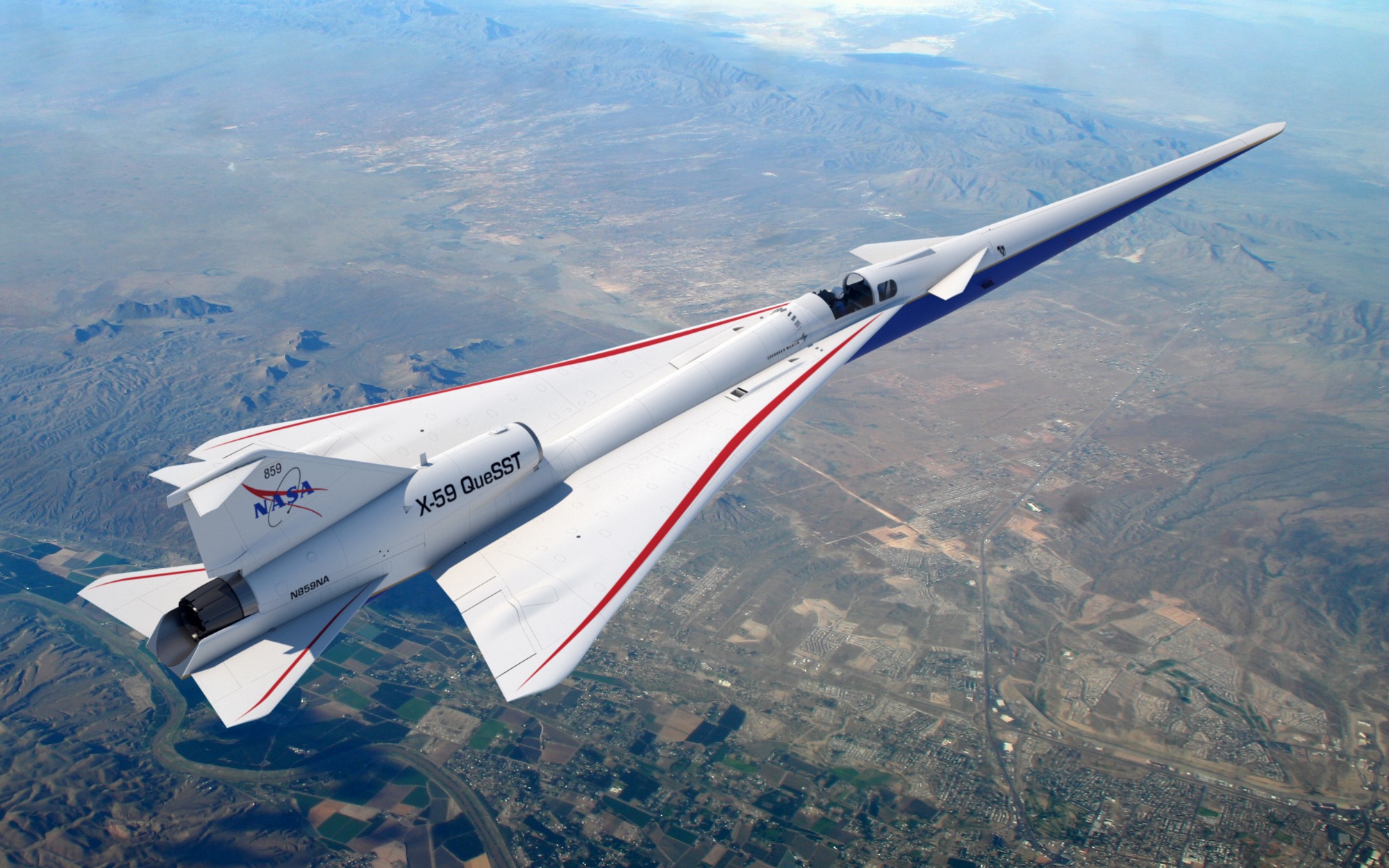
The one-of-a-kind experimental X-59 airplane will allow NASA to gather data that could revolutionize air travel, paving the way for a new generation of commercial aircraft that can travel faster than the speed of sound. The X-59 is expected to fly at 1.4 times the speed of sound, or 925 mph. Its design, shaping and technologies will allow the aircraft to achieve these speeds while generating a quieter sonic thump.
"This is a major accomplishment made possible only through the hard work and ingenuity from NASA and the entire X-59 team," said NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy. "In just a few short years we’ve gone from an ambitious concept to reality. NASA's X-59 will help change the way we travel, bringing us closer together in much less time."
The X-59 is at the center of NASA's Quesst mission, which focuses on providing data to help regulators reconsider rules that prohibit commercial supersonic flight over land. For the past 50 years, the U.S. and other nations have prohibited such flights due to the disturbance caused by loud, startling sonic booms on the communities below.
Its design, shaping and technologies could allow the aircraft to achieve these speeds while generating a quieter sonic thump.
"It's thrilling to consider the level of ambition behind Quesst and its potential benefits," said Bob Pearce, associate administrator for aeronautics research at NASA Headquarters in Washington. "NASA will share the data and technology we generate from this one-of-a-kind mission with regulators and with industry. By demonstrating the possibility of quiet commercial supersonic travel over land, we seek to open new commercial markets for U.S. companies and benefit travelers around the world."
NASA's Quesst team will now shift to its next steps in preparation for first flight, which will include integrated systems testing, engine runs, and taxi testing for the X-59.
The aircraft is set to take that maiden flight later this year, which will then be followed by its first quiet supersonic flight. The Quesst team will conduct several of the aircraft's flight tests at Skunk Works before transferring it to NASA's Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, which will serve as its base of operations.
Once NASA completes a series flight tests, the space agency will begin to fly the aircraft over several to-be-selected cities across the U.S., where it will collect input about the sound the X-59 generates and how people perceive it. NASA will provide that data to the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and international regulators.
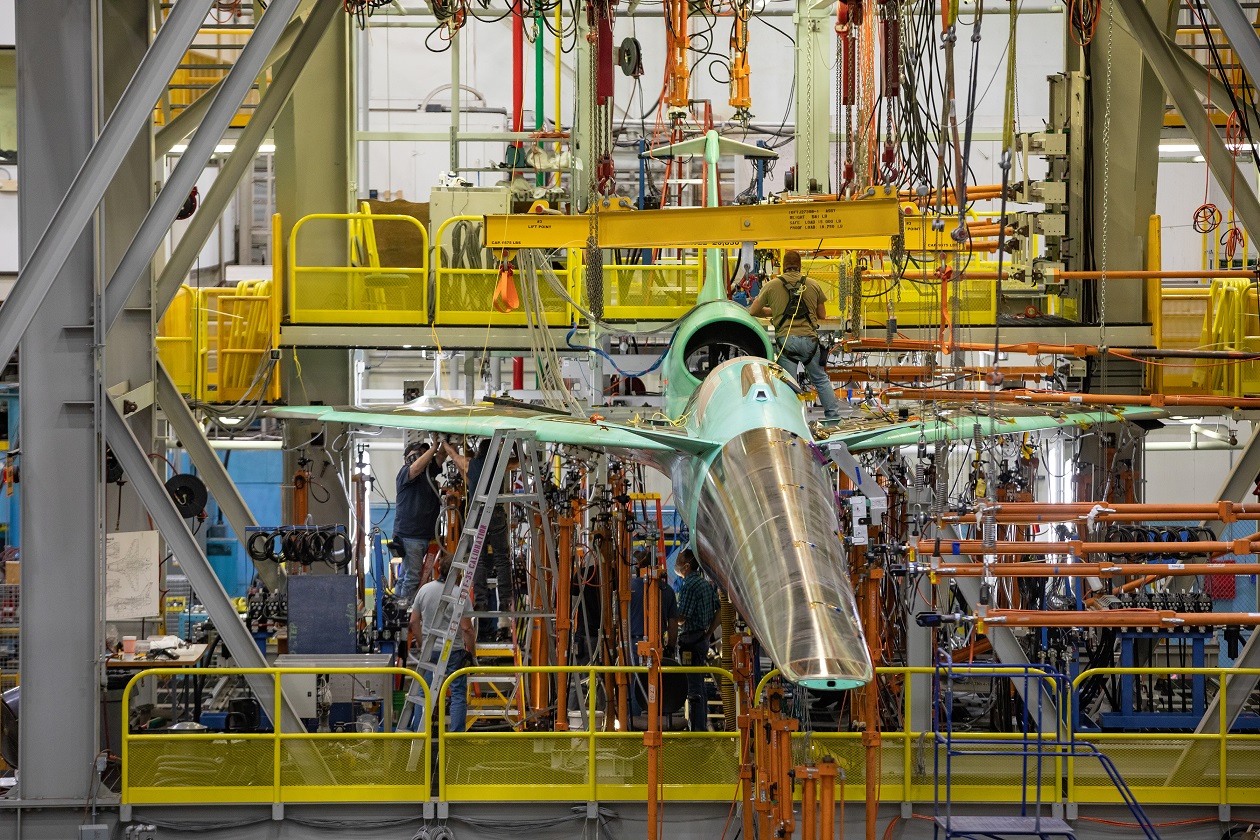

More Than a Prototype
The X-59 – like many NASA X-planes is a unique experimental airplane – and should not be considered a prototype. Rather it is a technology demonstrator that will be employed to inform future generations of quiet supersonic aircraft.
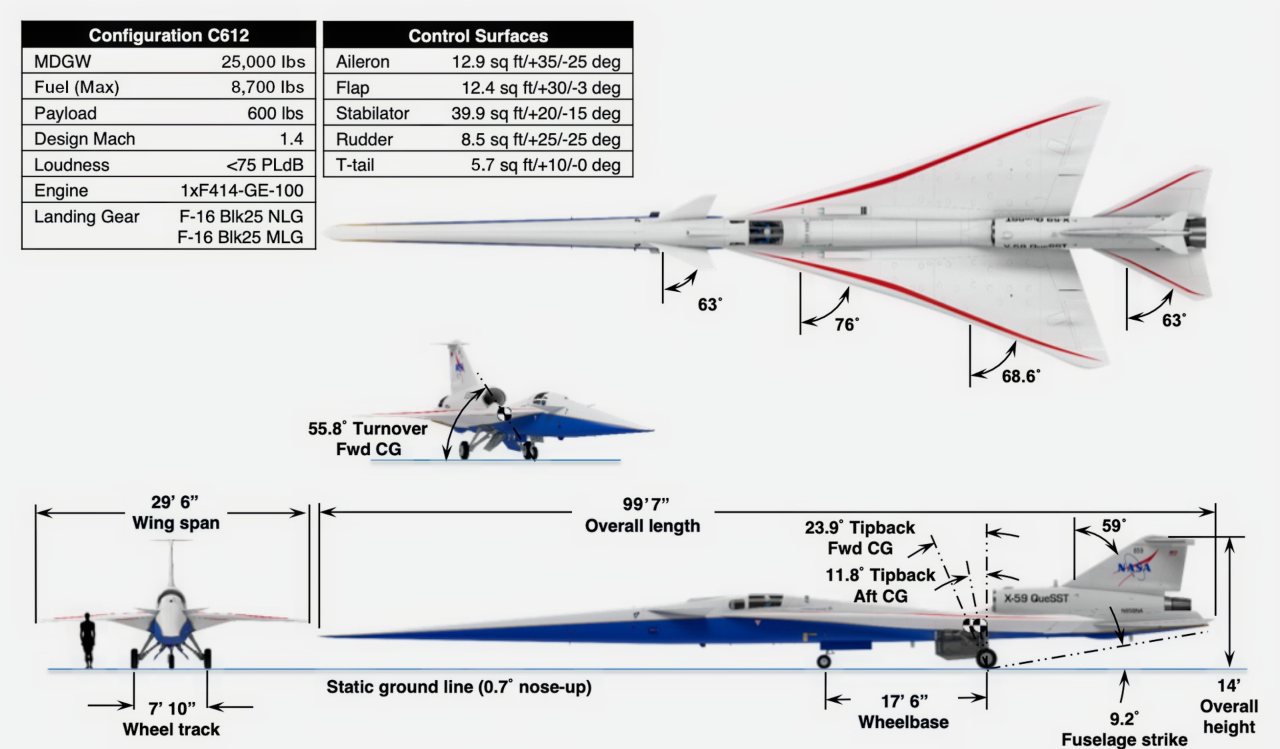
At 99.7 feet long and 29.5 feet wide, the X-59's shape and the technological advancements it houses will make quiet supersonic flight possible. This includes a thin, tapered nose that accounts for almost a third of its length and according to NASA will break up the shock waves that would ordinarily result in a supersonic aircraft causing a sonic boom. However, due to this unique configuration, the cockpit is located almost halfway down the length of the aircraft – and does not have a forward-facing window. Instead, the Quesst team developed the eXternal Vision System, a series of high-resolution cameras feeding a 4K monitor in the cockpit.
X-59 Configuration:
X-59 CONFIGURATION
Max Design Gross Weight...................................................... 25,000 lbs
Empty Weight ......................................................................... 14,990 lbs
Fuel........................................................................................... 8,700 lbs
Payload........................................................................................ 600 lbs
Design Mach....................................................................................... 1.4
Loudness ................................................................................. <75 PLdB
Engine............................................................................. 1xF414-GE-100
Landing Gear.................................................................F-16 Blk25 NLG
The Latest From the Skunk Works
The X-59 is the latest aircraft to come out of Lockheed Martin's Advanced Development Programs (ADP), formerly called Lockheed Advanced Development Projects.

Known by the official pseudonym "Skunk Works," it has been responsible for a number of aircraft designs, highly classified research and development programs, and exotic aircraft platforms. Known locations include the United States Air Force Plant 42 in Palmdale, CA, and the United States Air Force Plant 4 in Fort Worth, TX. Most notably, a majority of classified testing is also believed to be conducted at far more secret locations such as the Nevada Test Site.
Author Experience and Expertise: Peter Suciu
Peter Suciu is a Michigan-based writer. He has contributed to more than four dozen magazines, newspapers, and websites with over 3,200 published pieces over a twenty-year career in journalism. He regularly writes about military hardware, firearms history, cybersecurity, politics, and international affairs. Peter is also a Contributing Writer for Forbes and Clearance Jobs. You can follow him on Twitter: @PeterSuciu. You can email the author: [email protected].
All images are Creative Commons.


